
Read-Only Domain Controller or RODC is a type of domain controller which holds a read-only copy of active directory database and ideal in remote location where system security cannot be guaranteed.
Its allow the remote site to have local authentication point, without storing vulnerable data about every object in the domain. The only information stored on a read-only domain controller is that of users and computers it has been authorized to authenticate. Any other object that is queried or authorized against is forwarded by the read-only DC to writable domain controller.
To RODC or Not To RODC
The newly implemented Read-Only Domain Controller (RODC) in Windows Server 2008 provides a way to increase the security of servers whose physical security cannot be assured.
In addition, it can provide a way for local administrator privileges to be assigned to a user that you need to be an administrator at the local level, but who you do not want to allow a backstage pass into the domain-wide AD database via replication.
However, because the RODC intentionally limits its participation in the enterprise-wide AD structure, it is wise to limit its use to only those times when the additional level of security is required.
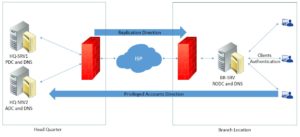
Why RODC?
- Physical security is not guaranteed in branch offices so read-only DCs are preferred instead of write-able DCs. If someone get an access to RODC, they won’t be able to make any changes because it holds a read-only copy of AD database. If they somehow change the database, they won’t be able to compromise the whole AD database because changes from RODC are not replicated to write-able DCs.
- There is a lack of trained IT staff in branch offices. An RODC is preferred, it is only used for users’ authentication and does not have time to time maintenance requirements including hardware updates, site-link changes, and user credential changes etc.
- Branch offices have poor network bandwidth connectivity with the head quarter. An RODC is deployed so the branch office users need not authenticate themselves from a write-able DC over a WAN link. This reduces the amount of time required to log on for branch office users.
Allowed and Denied RODC Password Replication Groups
RODC communicates with write-able DC for user authentication because by default account credentials are not cached locally on RODC. However, you can cache account credentials locally by adding users to allowed RODC password replication group. If a branch office users from this group log in, they will be authenticated locally provided the credentials have already been cached.
Similarly, to prevent privileged accounts (domain admins, enterprise admins etc.) from being cached locally on RODC for security purposes they are by default added to denied RODC password replication group.
Prerequisites
Before you start with installation and configuration of an RODC, make sure to check the following requirements.
- Administrator account has strong password
- Static IP is configured
- Latest updates from Microsoft are installed
- Firewall is turned off
- DNS server IP address in TCP/IPv4 properties is correct and it is pointing to DNS server of write-able DC (To verify, resolve the domain name from command prompt)

