Ransomware is a form of malicious software (or malware) that, once it’s taken over your computer, threatens you with harm, usually by denying you access to your data. The attacker demands a ransom from the victim, promising — not always truthfully — to restore access to the data upon payment.
Ransom and Software are words that are generated by
encrypting important data on PC and then encrypting the encrypted files and forcing the victim to pay the money
What are the symptoms of Ransomware infection?
- When Ransomware is infected, it creates a malicious file that performs encryption and sets the malicious file to run automatically when booting the PC.
- The next time you boot your PC, malicious file behavior causes your PC to be very slow and a window appears on the lower right corner that the firewall is off.
- It removes the trace that it executed and system restoration point, and encrypts the file (document, photo-oriented) which is the target of all paths shared with local PC
- It takes several minutes to several tens of minutes depending on the PC environment. In some cases, the file extension such as ccc, encrypted is changed or only the encryption is changed without changing the extension.
- The money request file (howto … / help … etc) is created in each folder and startup program.
- After completing the encryption, the malicious file deletes the traces that it was executed and the point of system restoration and performs the self-deletion.
If the money request information is not automatically displayed at boot time, and the encrypted file exists only in the shared folder, it is likely that it has been infected with another PC sharing the folder, not infecting the PC.
Some Ransomware variants may have other symptoms.
How can I prevent Ransomware?
Basic security practices must be followed.
- Keep your favorite SWs up to date, including Windows updates, IE browser, Adobe, and Office.
- If you can not check the update status of various SWs, you can check the status of the SW version at a glance by using functions such as vulnerability check of the Exploit Shield.
- Do not download files through untrusted sites such as file sharing sites such as torrents and personal blogs.
Use a reliable vaccine.
- Most commonly used vaccines are able to detect and repair most known Ransomware.
- Currently, pills also include Trojan.Ransom.cryptolocker, Trojan.Ransom.CryptoWall, Trojan.Ransom.TeslaCrypt, Trojan.Ransom.Filecoder, Trojan.Ransom.Chimera, etc.
- Diagnosis and treatment of Ransomware is possible with the same detection name.
* The Ransomware treatment concept in the vaccine is to remove the Ransomware malware, which does not mean to decrypt the encrypted document.
- In addition, Ransomware has been equipped with the Ransomware defense function in response to the latest Ransomware.
- Ransomware Detects and blocks malicious code before encrypting the user’s file, and can effectively cope with known Ransomware.
Make backups of important files a habit.
- Backup your important files to other storage media such as external hard disk, USB, not local PC. Even if you save to cloud service, real-time synchronization service is provided recently.
- Because local documents are synchronized right away, all of the information in the cloud can be encrypted.
- Especially, in a relatively business environment, there are many employees who need to manage and manage a lot of important documents.
- In this enterprise environment, the introduction of document backup solution and document centralization solution that can automatically backup the important data of the employees in real time can prevent the damage of Ransomware attack
Can I recover files encrypted with Ransomware?
Currently, Ransomware uses RSA 2048 asymmetric encryption when encrypting user files. The RSA 2048 encryption method can be used in domestic and overseas online banking and public institutions.
It is highly secure encryption. If the hacker does not have a decryption key, decryption is virtually impossible. A combination of digits and alphabetic characters and a 64-digit code,
64-squared, 78-digit number, so it takes decades to decode it with a supercomputer, so you can not actually decode it.
File recovery at system restore point (Windows Vista or later OS only)
File restoration is possible if restore point is created before Ransomware infection in Windows built-in system restoration. (Only Windows system files can be recovered, and user-generated document files are not recoverable.)
In recent years, there has been a ransomware that deletes the system restore point. In this case, it is impossible to recover by this method.
Some Ransomware can decrypt
In some Ransomware, some authors may be arrested or misrepresented and may be able to reveal their secret key. In this case, the encrypted file You can recover them.
What is Ransomware blocking function?
Ability to prevent the pellet from discovering and encrypting the file before the user’s PC is infected with Ransomware and the file is encrypted
How to block
Your PC is infected with Ransomware by a path of security vulnerability or attachment file.
Ransomware Prevents the user’s files from being encrypted by detecting and blocking the Ransomware from the pellets before the malicious code encrypts the files on the user’s PC. In addition to being able to effectively prevent Ransomware malware from encrypting files, the following diagnostics can be used to diagnose and repair Ransomware.
Do not download files through untrusted sites such as file sharing sites such as torrents and personal blogs.
Ransomware examples
While ransomware has technically been around since the ’90s, it’s only in the past five years or so that it’s really taken off, largely because of the availability of untraceable payment methods like Bitcoin.
- CryptoLocker, a 2013 attack that launched the modern ransomware age and infected up to 500,000 machines at its height
- TeslaCrypt, which targeted gaming files and saw constant improvement during its reign of terror
SimpleLocker, the first widespread ransomware attack that focused on mobile devices - WannaCry, which spread autonomously from computer to computer using EternalBlue, an exploit developed by the NSA and then stolen by hackers
- NotPetya, which also used EternalBlue and may have been part of a Russian-directed cyberattack against Ukraine
- Locky, which started spreading in 2016, was “similar in its mode of attack to the notorious banking software Dridex.”
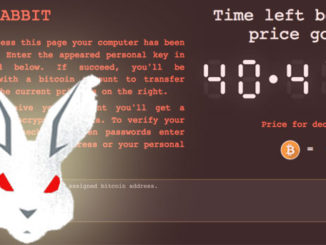
- BadRabbit, which started spreading in 2017, attacks multiple media outlets.
While ransomware attacks may be nearly impossible to stop, there are important data protection measures individuals and organizations can take to ensure that damage is minimal and recovery is a quick as possible. Strategies include compartmentalizing authentication systems and domains, keeping up-to-date storage snapshots outside the main storage pool and enforcing hard limits on who can access data and when access is permitted.
No Fields Found.