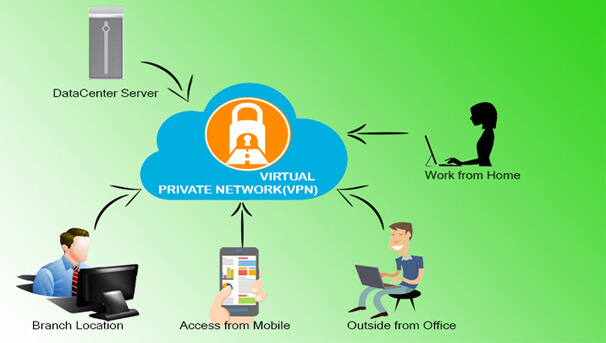
As a business grows, it might expand to multiple shops or offices across the country and around the world. To keep things running efficiently, the people working in those locations need a fast, secure and reliable way to share information across computer networks. In addition, traveling employees like salespeople need an equally secure and reliable way to connect to their business’s computer network from remote locations.
Where can you use a VPN?
Connecting two sites, a server to a remote site, or a single remote user to a site. These kinds of connections are the mainstay of the VPN. When security is needed an encryption with the desired key length, sharing of security certificates, or shared secret is all you may need.
VPN types
Remote Access VPN
Remote access VPN allows a user to connect to a private network and access its services and resources remotely. The connection between the user and the private network happens through the Internet and the connection is secure and private.
This type of VPN is useful for business and home users.
Home users, or private users of VPN, primarily use VPN services to bypass regional restrictions on the Internet and access blocked websites. Users conscious of Internet security also use VPN services to enhance their Internet security and privacy.
Site–to–Site VPN
Site-to-Site VPN is mostly used in the corporates. Companies, with offices in different geographical locations, use Site-to-site VPN to connect the network of one office location to the network at another office location.
Intranet based VPN
Multiple offices of the same company are connected using Site-to-Site VPN type, it is called as Intranet based VPN.
Extranet based VPN
Companies use Site-to-site VPN type to connect to the office of another company, it is called as Extranet based VPN. Basically, Site-to-site VPN create a virtual bridge between the networks at geographically distant offices and connect them through the Internet and maintain a secure and private communication between the networks.
Since Site-to-site VPN is based on Firewall, in this VPN type one firewall acts as a VPN Client and another firewall as a VPN Server. The communication between the two routers starts only after an authentication is validated between the two.
VPN protocols
VPN are based on different VPN security protocols. Each of these VPN protocols offer different features and levels of security.
Internet Protocol Security(IPSec)
IPSec is used to secure Internet communication across an IP network. IPSec secures Internet Protocol communication by authenticating the session and encrypts each data packet during the connection.
IPSec operates in two modes, Transport mode and Tunneling mode, to protect data transfer between two different networks. The transport mode encrypts the message in the data packet and the tunneling mode encrypts the entire data packet.
Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol (L2TP)
L2TP allows multiprotocol traffic to be encrypted and then sent over any medium that supports point-to-point datagram delivery, such as IP or asynchronous transfer mode (ATM).
Usually its combined with another VPN security protocol like IPSec to create a highly secure VPN connection.
Point–to–Point Tunneling Protocol (PPTP)
PPTP or Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol creates a tunnel and encapsulates the data packet. It uses a Point-to-Point Protocol (PPP) to encrypt the data between the connection. PPTP is one of the most widely used VPN protocol and has been in use since the time of Windows 95. Apart from Windows, PPTP is also supported on Mac and Linux.
Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) and Transport Layer Security (TLS)
SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) and TLS (Transport Layer Security) create a VPN connection where the web browser acts as the client and user access is restricted to specific applications instead of entire network. SSL and TLS protocol is most commonly used by online shopping websites and service providers. Web browsers switch to SSL with ease and with almost no action required from the user, since web browsers come integrated with SSL and TLS. SSL connections have https in the beginning of the URL instead of http.
